For business leaders in Texas's core industries like Energy, Manufacturing, Logistics, and Construction, operational resilience is a strategic imperative. The state's dynamic economy is matched by its volatile weather, from Gulf Coast hurricanes to statewide freezes, making effective facility management a critical line of defense. Strong facility management transforms physical assets from potential liabilities into resilient cornerstones of business continuity, directly impacting uptime and profitability.
This article moves beyond theory to provide a clear blueprint of eight critical facility management best practices. We will outline actionable, data-driven strategies designed to help you assess vulnerabilities, prepare for extreme weather events, and mitigate operational risks unique to the Texas landscape. You will find practical steps for implementing preventive maintenance, integrating technology, and ensuring safety protocols are robust and reliable. The insights provided are designed to empower informed decision-making and fortify your operations against disruption. Each practice is a key component in building a more resilient and efficient enterprise prepared for any challenge.
1. Master Proactive Maintenance for Uninterrupted Operations
Shifting from a reactive “fix-it-when-it-breaks” model to a proactive strategy is a cornerstone of modern facility management best practices. This approach involves scheduled inspections, preventive maintenance, and strategic repairs based on equipment usage, operating conditions, and manufacturer guidelines. For Texas industries, where an equipment failure during an extreme heatwave or freeze can halt production, this strategy is non-negotiable.
Proactive maintenance guarantees operational uptime when it matters most by addressing potential failures before they occur. The digital backbone for this is a Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS), which is crucial for tracking assets, scheduling tasks, and analyzing failure patterns. This allows you to move beyond simple preventive schedules to predictive maintenance, using data to anticipate needs and optimize resource allocation.
Implementation in Action
- Petrochemical: A Gulf Coast plant uses predictive maintenance with sensor data on its cooling systems. This allows them to preemptively service components before the summer heat, preventing costly shutdowns like those experienced during past heatwaves. The U.S. chemical industry, a major presence in Texas, experienced losses estimated at $1 billion from the 2021 winter storm Uri, underscoring the high cost of equipment failure.
- Logistics: A Houston warehouse implemented a CMMS to schedule routine maintenance on conveyor systems and loading dock doors. This simple shift reduced downtime by 30% and helped them avoid critical shipping delays during peak seasons.
The following infographic highlights the significant business impact of adopting a proactive maintenance strategy.
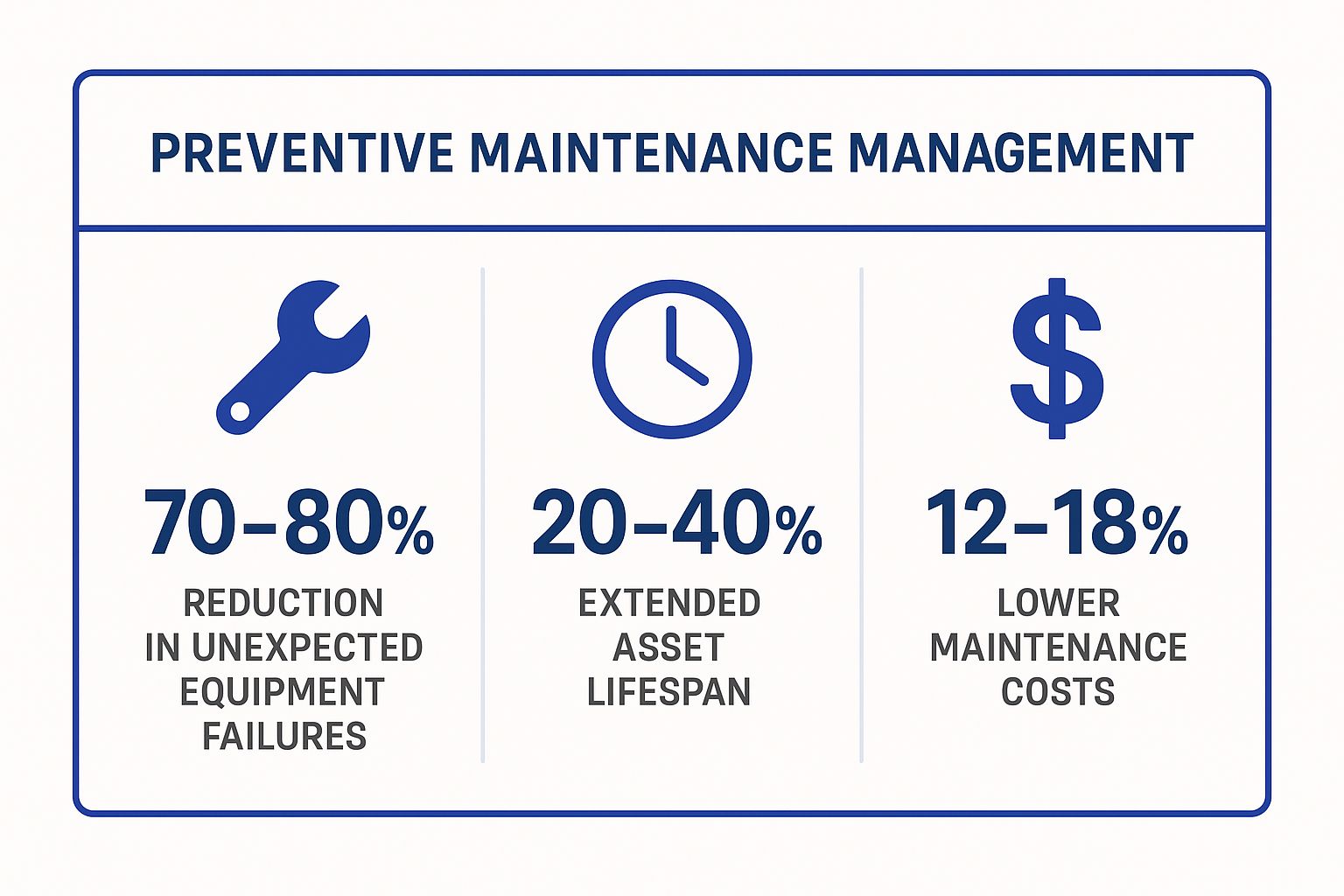
These figures demonstrate that proactive maintenance is a powerful investment, directly boosting asset longevity and operational stability while reducing long-term costs.
Actionable Tips for Success
To effectively implement this practice, focus on a few key areas:
- Prioritize Critical Assets: Use your risk assessment to identify and prioritize essential equipment like backup generators, HVAC systems, and flood pumps that are vital during extreme weather.
- Leverage a CMMS: Invest in a robust CMMS to track all maintenance activities, manage work orders, and analyze performance data.
- Establish Clear KPIs: Monitor metrics like Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) and Mean Time To Repair (MTTR) to measure program effectiveness.
- Train Your Team: Ensure all staff are thoroughly trained on new procedures, checklists, and the technologies you implement.
2. Space Optimization and Utilization Analysis
A strategic approach to maximizing the efficiency of physical spaces is a critical facility management best practice, shifting focus from mere square footage to data-driven insights. This practice involves measuring occupancy rates, understanding space usage patterns, and reconfiguring layouts to align with actual needs rather than assumptions. For Texas manufacturing and logistics hubs, optimizing floor space can directly improve production flow and supply chain velocity.
This analytical method ensures every square foot of your facility adds value, whether it's a corporate office, a manufacturing floor, or a logistics hub. By using tools like occupancy sensors and analytics platforms, facility managers can make informed decisions that directly impact operational efficiency and the bottom line. This data-driven approach allows for smarter, more flexible space designs that support diverse work styles and operational demands. To learn more about how this impacts your broader goals, explore our insights on operational efficiency improvement on climaterisknow.com.

Implementation in Action
- Manufacturing: A North Texas automotive parts manufacturer used space utilization analysis to reconfigure its production line. This change improved workflow, reduced material transit times by 15%, and increased overall output without expanding their physical footprint.
- Logistics: A distribution center near the Port of Houston leveraged data to optimize its racking and storage layout, increasing its storage capacity by 20% within the existing facility and improving order fulfillment speed.
These examples show that strategic space analysis is not just about cutting costs; it's about creating more effective, collaborative, and productive environments.
Actionable Tips for Success
To effectively implement this practice, focus on a few key areas:
- Establish a Baseline: Conduct a 3-6 month baseline study to collect data on current space usage before making any significant changes.
- Engage Operations Teams: Involve your team in the process to understand their specific work styles, needs, and pain points regarding the current layout.
- Create Activity Zones: Designate different zones for specific operational functions to streamline processes and reduce bottlenecks.
- Implement Gradually: Roll out changes in phases rather than a complete overhaul to minimize disruption and gather feedback along the way.
- Set Clear Targets: Establish clear space utilization targets (e.g., improve production floor efficiency by 10%) to measure success and guide adjustments.
3. Implement an Integrated Workplace Management System (IWMS)
Moving beyond siloed spreadsheets and disjointed software is a critical facility management best practice for complex operations. An Integrated Workplace Management System (IWMS) provides a single source of truth, consolidating real estate, infrastructure management, operations, and sustainability initiatives into one unified platform. This centralized approach enables data-driven decisions and strategic portfolio management. For Texas industries managing vast physical footprints, an IWMS is the digital backbone for efficiency and control.
An IWMS transforms facility management from a collection of reactive tasks into a cohesive, strategic function. By integrating data from various departments, it offers a holistic view of asset performance, space utilization, and operational costs. This allows managers to identify inefficiencies, automate routine workflows, and forecast future needs with far greater accuracy, optimizing resource allocation and supporting long-term business goals.
Implementation in Action
- Energy Sector: A major energy company with operations across the Permian Basin implemented an IWMS to manage its distributed assets. This resulted in a 15% reduction in maintenance dispatch times and improved compliance with Texas Railroad Commission (RRC) regulations.
- Federal Government: The U.S. General Services Administration (GSA) uses an IWMS to manage its federal real estate portfolio of 370 million square feet, enhancing its ability to track asset performance and manage leases efficiently.
- Construction: A large Texas-based construction firm uses an IWMS to manage equipment and asset allocation across multiple job sites, improving asset utilization by 25% and reducing rental costs.
These examples show how an IWMS drives significant ROI by reducing operational costs, improving asset performance, and providing the data needed for strategic facility planning.
Actionable Tips for Success
To successfully implement an IWMS, a structured approach is essential:
- Conduct a Needs Assessment: Before selecting a vendor, thoroughly analyze your current processes and identify key pain points to ensure the chosen platform aligns with your goals.
- Secure Executive Buy-In: An IWMS is a significant investment. Secure commitment from leadership by presenting a clear business case focused on long-term ROI and operational resilience.
- Plan a Phased Rollout: Start with core modules like maintenance and space management. Expand to other functions gradually to manage the change and ensure user adoption.
- Prioritize Data Hygiene: Clean and standardize all facility data before migrating it to the new system. Accurate data is the foundation of a successful IWMS implementation.
4. Energy Management and Sustainability Programs
Integrating a strategic framework for energy management is a critical component of modern facility management best practices. This approach moves beyond simple cost-cutting to encompass a comprehensive strategy for monitoring, controlling, and reducing energy consumption while advancing corporate sustainability goals. For energy-intensive Texas industries, where utility costs can be substantial and the ERCOT grid faces strain during extreme weather, this practice is essential for both financial health and operational continuity.
Effective energy management combines technology, such as building automation systems and IoT sensors, with policy and behavioral changes to minimize environmental impact. This holistic view is crucial for reducing operational costs, meeting regulatory requirements, and enhancing brand reputation. It transforms facilities from passive energy consumers into efficient, high-performing assets that contribute directly to the bottom line.

Implementation in Action
- Manufacturing: A Texas-based manufacturing plant implemented a comprehensive energy audit, leading to an LED lighting retrofit and HVAC optimization. These changes reduced their energy intensity by over 25%, delivering significant cost savings and reducing their strain on the local grid during peak demand.
- Logistics: A large distribution center near Dallas achieved LEED certification by installing a solar array on its roof and implementing smart controls for lighting and climate. This not only lowered their energy bills but also helped them secure contracts with clients who prioritize sustainable supply chain partners.
These examples show that a dedicated focus on energy and sustainability delivers a powerful return on investment, improving operational efficiency and long-term resilience.
Actionable Tips for Success
To build a successful energy management program, concentrate on these key initiatives:
- Conduct an Energy Audit: Begin with a professional audit to benchmark your current consumption and identify the most significant opportunities for improvement, from quick wins to capital projects.
- Set Measurable Goals: Establish specific, time-bound targets, such as a "20% reduction in electricity consumption in 3 years," to guide your efforts and measure success.
- Leverage Technology: Implement building automation systems (BAS) and smart meters to track energy use in real-time, automate controls, and identify anomalies.
- Engage Occupants: Foster a culture of conservation through awareness campaigns and clear communication, as employee behavior can significantly impact energy use.
5. Comprehensive Risk Management and Safety Protocols
A systematic approach to identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks is fundamental to modern facility management best practices. This practice moves beyond basic safety compliance, creating an integrated framework that protects people, assets, and operational continuity. It encompasses physical security, emergency preparedness for events like hurricanes and freezes, health and safety protocols, and robust business continuity planning.
For Texas industries, where operational hazards are compounded by environmental risks, this proactive stance is critical. Effective risk management uses data to anticipate threats, from equipment failure and workplace accidents to cybersecurity breaches in connected building systems. By embedding safety into every function, facilities can build resilience against disruptions, ensuring a secure environment for all stakeholders. This structured methodology is essential for maintaining operational integrity and regulatory compliance with bodies like OSHA and the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ).
Implementation in Action
- Energy & Petrochemical: Following Hurricane Harvey, which caused an estimated $1.25 billion in damages to the refining sector, many Gulf Coast facilities upgraded their emergency response plans. They implemented elevated storage for critical equipment and enhanced flood barrier systems, significantly reducing their vulnerability to future storm surges.
- Construction: A general contractor in Austin reduced its recordable incident rate by 40% by implementing a behavior-based safety program and conducting daily "toolbox talks" focused on site-specific hazards.
These examples show how a dedicated focus on risk management directly translates to safer, more efficient, and resilient operations.
Actionable Tips for Success
To build a robust risk and safety framework, concentrate on these key actions:
- Conduct Annual Risk Assessments: Systematically review all potential operational, environmental, and security hazards to identify vulnerabilities.
- Develop an Emergency Action Plan (EAP): Create detailed, site-specific plans for extreme weather events common in Texas, including hurricanes, floods, and winter storms.
- Train and Drill Regularly: Ensure all personnel are trained on emergency procedures, including proactive measures to prevent electrical fires, and conduct quarterly drills to test response plans.
- Establish a Clear Chain of Command: Define roles and responsibilities for crisis situations to ensure decisive and coordinated action.
- Document and Analyze Incidents: Maintain detailed records of all incidents and near-misses to identify patterns and inform protocol updates. To deepen your understanding, you can learn more about operational risk management on climaterisknow.com.
6. Data-Driven Performance Measurement and KPIs
Transforming facility management from a cost center into a strategic business function hinges on a systematic approach to performance measurement. This practice involves defining, tracking, and analyzing Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to measure effectiveness, efficiency, and value. By quantifying performance, facility managers can identify improvement opportunities, justify investments, and clearly demonstrate their return on investment to stakeholders.
This data-driven approach is a core component of modern facility management best practices. It moves beyond simple observation to leverage real-time dashboards and predictive analytics, allowing for continuous improvement. For Texas industries, where operational efficiency directly impacts profitability, using KPIs to monitor everything from energy consumption to work order completion times is essential for maintaining a competitive edge.
Implementation in Action
- Manufacturing: A large food processing plant in Texas uses a real-time KPI dashboard to monitor equipment uptime, energy consumption per unit produced, and maintenance costs. This data-driven oversight helped them identify an underperforming cooling unit, which, once replaced, improved energy efficiency by 18%.
- Agriculture: A major agricultural producer tracks water usage and irrigation system performance across thousands of acres. By analyzing this data, they can optimize water allocation, comply with local water district regulations, and reduce operational costs during drought conditions.
These examples show how quantifiable metrics empower organizations to optimize resources and make informed, strategic decisions. A similar approach using data analytics can be applied in other business areas to manage risk and improve outcomes. For further reading, you can learn more about data analytics in risk management.
Actionable Tips for Success
To effectively implement this practice, focus on a few key areas:
- Start Small and Focused: Begin with 5-10 critical KPIs that directly align with your organization's strategic objectives, such as reducing energy costs or improving equipment uptime.
- Establish a Baseline: Before setting targets, measure your current performance to establish a clear baseline. This makes progress measurable and meaningful.
- Automate Data Collection: Wherever possible, use CMMS or building automation systems to automate data collection. This reduces manual effort and improves accuracy.
- Create Audience-Specific Dashboards: Develop different visual dashboards for various stakeholders. Executives may need high-level financial summaries, while operations teams need detailed work order metrics.
7. Proactive Vendor and Contract Management
Shifting vendor relationships from transactional exchanges to strategic partnerships is a vital component of modern facility management best practices. This approach involves rigorous selection, continuous performance monitoring, and collaborative management of all external service providers. Given that vendor-provided services can account for a significant portion of a facility’s operating budget, optimizing these relationships is crucial for cost control, service quality, and risk mitigation.
A proactive vendor management strategy ensures that contractors and suppliers act as extensions of your own team, aligning their performance with your operational goals. This is particularly important for Texas industries, where the reliability of a key vendor, like an HVAC or generator maintenance firm, can be the difference between operational continuity and a costly shutdown during an extreme weather event. The goal is to build a resilient network of high-performing partners who deliver consistent value.
Implementation in Action
- Petrochemical: A refinery along the Texas Gulf Coast established a strategic partnership with its primary industrial cleaning vendor. By co-developing safety protocols and maintenance schedules, they reduced turnaround times by 10% and improved safety compliance scores.
- Logistics: A statewide logistics company consolidated its fleet maintenance contracts under a single provider with clear performance KPIs. This led to a 15% reduction in vehicle downtime and a streamlined invoicing process, saving significant administrative overhead.
Effective vendor management directly impacts your bottom line and operational resilience, turning a major cost center into a source of competitive advantage. For comprehensive guidance on strengthening your external partnerships and achieving operational excellence, consider integrating leading vendor management best practices into your strategy.
Actionable Tips for Success
To effectively implement this practice, focus on a few key areas:
- Develop Detailed RFPs: Create requests for proposals with a clear scope, specific expectations, and transparent evaluation criteria to attract the right partners.
- Embed KPIs in Contracts: Include measurable performance metrics, along with clear penalties for non-compliance and incentives for exceptional service, directly into your contracts.
- Conduct Quarterly Reviews: Schedule regular business reviews with strategic vendors to discuss performance, address challenges, and align on future goals. This is a critical part of a strong supply chain risk management strategy.
- Balance Cost and Quality: Look beyond the lowest bid. Evaluate vendors on the total cost of ownership, considering their reliability, quality, and the long-term value of the relationship.
8. Occupant Experience and Engagement Programs
Superior facility management best practices extend beyond asset maintenance to encompass the human element within the building. This holistic approach prioritizes the needs, satisfaction, and wellbeing of occupants, transforming functional spaces into environments that boost productivity and talent retention. For competitive Texas industries, where attracting and keeping skilled labor is critical, creating a positive occupant experience is a powerful business strategy.
This practice involves actively listening to occupant feedback, implementing wellness programs, and leveraging technology to create a seamless, comfortable, and engaging workplace. It recognizes that the physical environment directly impacts employee morale, collaboration, and overall performance. By focusing on the user, facility managers shift from being cost centers to value drivers, directly contributing to organizational success.
Implementation in Action
- Technology: A major tech firm's Austin campus focused on occupant experience, integrating smart building tech that allows for personalized environmental controls. This resulted in a 25% increase in collaboration and a 92% employee satisfaction rating.
- Corporate: Unilever's offices incorporate WELL Building Standard principles, which prioritize air quality, lighting, and biophilic design. The company reported 33% fewer sick days and a notable 15% improvement in productivity.
These examples show that investing in occupant-centric programs provides a tangible return on investment through improved operational efficiency and a stronger company culture.
Actionable Tips for Success
To effectively implement this practice, focus on a few key areas:
- Establish Feedback Loops: Conduct regular satisfaction surveys and create multiple feedback channels, such as a dedicated app, email, or suggestion boxes.
- Respond and Communicate: Visibly respond to feedback with clear action plans and updates to show occupants their input is valued.
- Invest in Self-Service Tools: Deploy intuitive platforms that allow employees to book spaces, control their environment, and request services easily.
- Train for Empathy: Ensure facility management staff receive customer service and empathy training to improve interactions with occupants.
Facility Management Best Practices Comparison
| Item | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Preventive Maintenance Management | Medium to High: 3-18 months, requires training | Moderate to High: CMMS, IoT sensors, trained staff | Reduces failures 70-80%, extends asset life 20-40%, lowers costs 12-18% | Critical assets maintenance, industrial & commercial facilities | Reduced downtime, extended asset life, improved safety |
| Space Optimization and Utilization Analysis | Medium: 3-6 month study plus ongoing adjustments | Moderate: occupancy sensors, analytics platforms | 15-30% real estate cost savings, improved employee satisfaction | Offices adopting hybrid work, real estate cost reduction | Data-driven space use, better collaboration, lower energy use |
| Integrated Workplace Management Systems (IWMS) | High: 6-18 months, complex implementation | High: software investment, change management | 20-30% efficiency gains, cost reductions, centralized data | Large portfolios, multi-site management | Single platform, automation, improved compliance & insights |
| Energy Management and Sustainability Programs | Medium to High: audits, retrofits, ongoing management | Moderate to High: tech upgrades, specialized expertise | 15-30% energy reduction, carbon footprint lowering, cost savings | Sustainability goals, regulatory compliance, energy cost control | Lower energy costs, enhanced reputation, regulatory compliance |
| Comprehensive Risk Management and Safety Protocols | Medium to High: ongoing updates, audits, training | High: security systems, training, protocols | Reduced liability, lowered incidents (20-40%), improved preparedness | High-risk environments, safety-critical facilities | Reduced risks, compliance, business continuity |
| Data-Driven Performance Measurement and KPIs | Medium: set up dashboards, analytics, and reporting | Moderate: analytics tools, skilled staff | Clear performance insights, 15-20% cost efficiency improvements | Facilities needing continuous improvement and ROI measurement | Objective metrics, data-driven decisions, improved accountability |
| Proactive Vendor and Contract Management | Medium: requires policy updates, ongoing reviews | Moderate: vendor management tools, staff time | 10-25% procurement cost savings, improved service quality | Organizations with high outsourced FM spend | Cost control, risk mitigation, stronger vendor relationships |
| Occupant Experience and Engagement Programs | Medium: surveys, tech platform deployment, programs | Moderate to High: amenities, communication tools | 5-15% productivity gain, higher satisfaction and retention | Employee-centric workplaces | Enhanced occupant satisfaction, productivity, talent retention |
Building a Resilient Future for Your Texas Operations
The journey from a reactive, problem-solving facility management model to a proactive, strategic one is the defining characteristic of industry leaders across Texas. The eight facility management best practices we've explored, from implementing a robust Preventive Maintenance Management program to championing Occupant Experience and Engagement, are not isolated tactics. Instead, they form a powerful, interconnected framework for building operational resilience, efficiency, and long-term value.
From Managing Buildings to Driving Business Value
Moving beyond the day-to-day firefighting is essential. By embracing Integrated Workplace Management Systems (IWMS), you centralize data, break down information silos, and empower your team with a single source of truth. This technological foundation enables more effective Space Optimization, ensuring every square foot of your manufacturing plant, distribution center, or petrochemical facility contributes directly to your bottom line. Similarly, a focus on Energy Management and Sustainability isn't just about environmental stewardship; it's a critical cost-control strategy that strengthens your financial resilience against volatile energy markets, a key concern for Texas operators.
The Foundation of Resilience: Proactive and Data-Informed Decisions
At its core, adopting these best practices means shifting your entire operational mindset. It’s about using data-driven performance metrics to move from guesswork to informed strategy, ensuring your decisions are both effective and justifiable. It’s about transforming vendor relationships from transactional exchanges into strategic partnerships through proactive contract management, guaranteeing quality, and mitigating supply chain risks.
Most importantly, it’s about embedding a culture of safety and preparedness through Comprehensive Risk Management and Safety Protocols. For Texas industries facing challenges from extreme weather events, this is non-negotiable. A proactive approach to safety doesn't just prevent incidents; it protects your most valuable assets: your people.
By weaving these principles into the fabric of your operations, you do more than just manage a facility. You are building a competitive advantage. You are creating a secure, efficient, and resilient enterprise capable of thriving in the dynamic Texas economy. The true value of mastering these facility management best practices lies not just in cost savings or operational uptime, but in securing your organization's future, safeguarding your workforce, and cementing your position as a leader in your sector. The time to build that future is now.
Ready to transform your risk management from a manual process into a strategic advantage? Sentinel Shield provides the advanced analytics and scenario-planning tools you need to assess your operational vulnerabilities and implement proactive mitigation strategies. Take the next step in building a truly resilient Texas enterprise by visiting Sentinel Shield today.

